Business / By Gennaro Cuofano / October 24, 2023
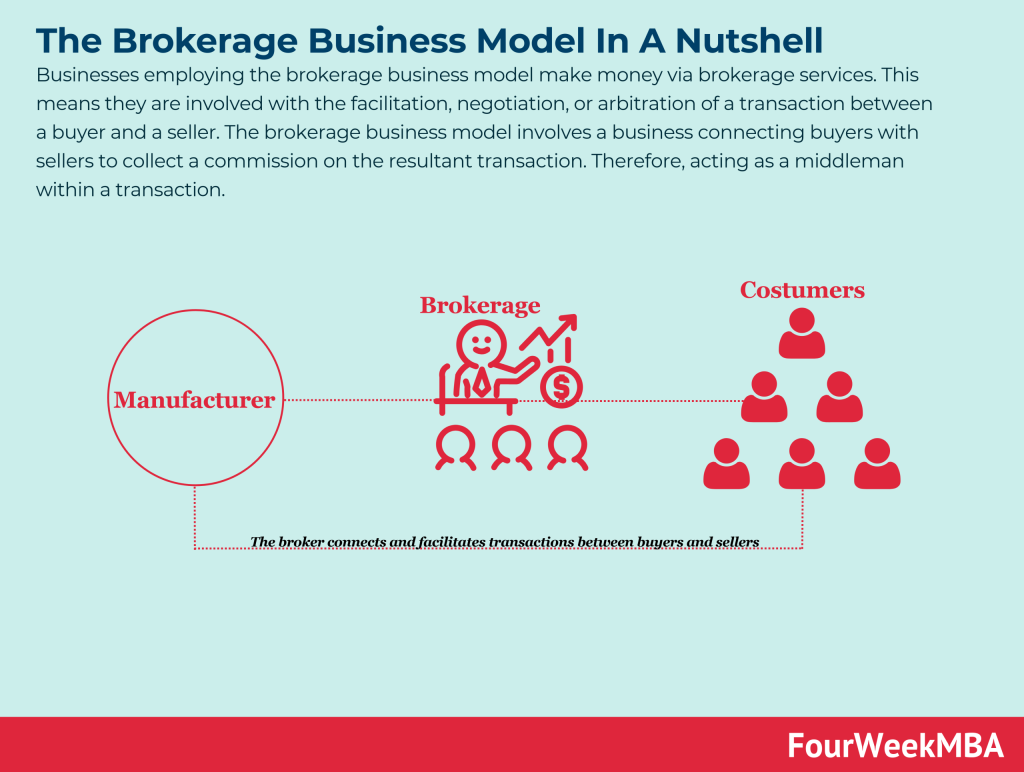
Businesses employing the brokerage business model make money via brokerage services. This means they are involved with the facilitation, negotiation, or arbitration of a transaction between a buyer and a seller. The brokerage business model involves a business connecting buyers with sellers to collect a commission on the resultant transaction. Therefore, acting as a middleman within a transaction.
Aspect
Explanation
Brokerage Business Model
A Brokerage Business Model is a type of business model where a company or individual acts as an intermediary or broker between buyers and sellers of goods, services, or assets. Brokers facilitate transactions and earn a fee, commission, or spread for their services. This model is prevalent in various industries, including real estate, finance, e-commerce, and more.
Key Concepts
– Intermediary Role: Brokers play a crucial intermediary role, connecting buyers and sellers who may not have direct access to each other. – Commission or Fee: Brokers earn revenue through commissions, fees, or spreads on transactions they facilitate. – Market Expertise: Successful brokers often have deep market knowledge and expertise in their respective industries. – Trust and Reputation: Building trust and a positive reputation are vital for attracting clients in the brokerage business.
Examples
– Real Estate Brokerage: Real estate agents and brokers connect property buyers and sellers, earning a commission on the sale. – Stockbrokerage: Stockbrokers facilitate the buying and selling of stocks and securities for investors, charging a commission per trade. – Insurance Brokerage: Insurance brokers help individuals and businesses find suitable insurance coverage and earn a commission from insurers. – Freight Brokerage: Freight brokers match shippers with carriers and charge a fee for arranging transportation. – Art Brokerage: Art brokers connect art buyers and sellers, earning a commission on art sales.
Applications
– Financial Services: Brokerages are integral to financial markets, enabling individuals and institutions to trade stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies. – Real Estate: Real estate brokerages assist in buying, selling, and renting properties. – E-commerce: Online marketplaces often operate on a brokerage model, connecting buyers and sellers of various products. – Import and Export: Import/export brokers facilitate international trade by connecting buyers and sellers across borders.
Challenges
– Competition: Brokerage industries can be highly competitive, with many players vying for clients. – Regulation: Some brokerage sectors, like finance, are subject to strict regulatory frameworks. Compliance is essential. – Market Fluctuations: Economic and market fluctuations can impact brokerage businesses, affecting transaction volumes and revenue. – Trust: Establishing trust and credibility with clients is crucial in the brokerage business.
Mitigation
– Specialization: Specializing in a niche market can help brokers stand out and attract clients looking for expertise. – Technology: Embracing technology can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the client experience. – Compliance: Staying informed about industry regulations and complying with them is essential. – Customer Service: Providing exceptional customer service can build trust and loyalty.
Scientific Significance
Brokerage business models illustrate the significance of intermediaries in facilitating trade and transactions in various industries. They also highlight the role of trust and expertise in these relationships.
Conclusion
Brokerage business models serve as essential intermediaries, connecting buyers and sellers across diverse industries. They thrive on market expertise, trust, and the ability to efficiently match parties to transactions. While competitive and subject to challenges, brokerages continue to play a vital role in global commerce.
Understanding the brokerage business model
Brokerage businesses usually charge a commission or fee to one or both parties in exchange for services rendered.
Many such companies have also adopted a zero-commission policy, instead of making money from investments and the difference in price between what they charge buyers and what they charge sellers.
Advances in eCommerce have allowed the brokerage business model to thrive since virtually any product or service can now be ordered online.
Brokerage businesses are common in the real estate, finance, retail, travel, and online marketplace industries, to name a few.